Retrieval-Augmented Technology is altering the best way LLMs faucet into exterior information. The issue is that a whole lot of builders misunderstand what RAG truly does. They give attention to the doc sitting within the vector retailer and assume the magic begins and ends with retrieving it. However indexing and retrieval aren’t the identical factor in any respect.
Indexing is about the way you select to symbolize information. Retrieval is about what elements of that information the mannequin will get to see. When you acknowledge that hole, the entire image shifts. You begin to understand how a lot management you even have over the mannequin’s reasoning, pace, and grounding.
This information breaks down what RAG indexing actually means and walks by way of sensible methods to design indexing methods that truly assist your system assume higher, not simply fetch textual content.
What’s RAG indexing?
RAG indexing is the premise of retrieval. It’s the course of of remodeling uncooked information into numerical information that may then be searched by way of similarity queries. This numerical information is named embeddings, and embeddings captures which means, quite than simply floor stage textual content.
Take into account this like constructing a searchable semantic map of your information base. Every chunk, abstract, or variant of a question turns into a degree alongside the map. The extra organized this map is, the higher your retriever can establish related information when a consumer asks a query.
In case your indexing is off, corresponding to in case your chunks are too massive, the embeddings are capturing noise, or your illustration of the info doesn’t symbolize consumer intent, then no LLM will assist you to very a lot. The standard of retrieval will at all times depend upon how successfully the info is listed, not how nice your machine studying mannequin is.
Why it Issues?
You aren’t constrained to retrieving solely what you index. The ability of your RAG system is how successfully your index displays which means and never textual content. Indexing articulates the body by way of which your retriever sees the information.
Whenever you match your indexing technique to your information and your consumer want, retrieval will get sharper, fashions will hallucinate much less, and consumer will get correct completions. A well-designed index turns RAG from a retrieval pipeline into an actual semantic reasoning engine.
RAG Indexing Methods That Truly Work
Suppose we have now a doc about Python programming:
Doc = “”” Python is a flexible programming language extensively utilized in information science, machine studying, and internet growth. It helps a number of paradigms and has a wealthy ecosystem of libraries like NumPy, pandas, and TensorFlow. “””
Now, let’s discover when to make use of every RAG indexing technique successfully and tips on how to implement it for such content material to construct a performant retrieval system.
1. Chunk Indexing
That is the start line for many RAG pipelines. You cut up giant paperwork into smaller, semantically coherent chunks and embed every one utilizing some embedding mannequin. These embeddings are then saved in a vector database.
Instance Code:
# 1. Chunk Indexing
def chunk_indexing(doc, chunk_size=100):
phrases = doc.cut up()
chunks = []
current_chunk = []
current_len = 0
for phrase in phrases:
current_len += len(phrase) + 1 # +1 for house
current_chunk.append(phrase)
if current_len >= chunk_size:
chunks.append(” “.be a part of(current_chunk))
current_chunk = []
current_len = 0
if current_chunk:
chunks.append(” “.be a part of(current_chunk))
chunk_embeddings = [embed(chunk) for chunk in chunks]
return chunks, chunk_embeddings
chunks, chunk_embeddings = chunk_indexing(doc_text, chunk_size=50)
print(“Chunks:n”, chunks)
Greatest Practices:
All the time preserve the chunks round 200-400 tokens for brief type textual content or 500-800 for lengthy type technical content material.
Ensure that to keep away from splitting mid sentences or mid paragraph, use logical, semantic breaking factors for higher chunking.
Good to make use of overlapping home windows (20-30%) in order that context at boundaries isn’t misplaced.
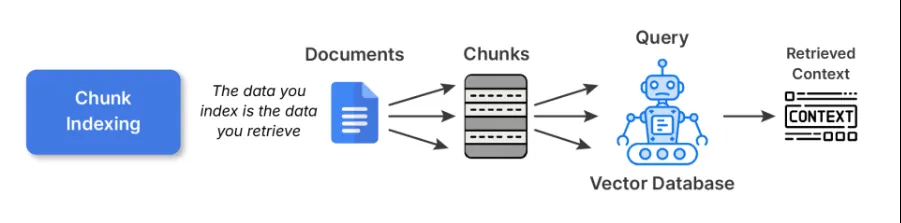
Commerce-offs: Chunk indexing is easy and general-purpose indexing. Nonetheless, greater chunks can hurt retrieval precision, whereas smaller chunks can fragment context and overwhelm the LLM with items that don’t match collectively.
Learn extra: Construct RAG Pipeline utilizing LlamaIndex
2. Sub-chunk Indexing
Sub-chunk indexing serves as a layer of refinement on prime of chunk indexing. When embedding the conventional chunks, you additional divide the chunk into smaller sub-chunks. Whenever you need to retrieve, you examine the sub-chunks to the question, and as soon as that sub-chunk matches your question, the complete father or mother chunk is enter into the LLM.
Why this works:
The sub-chunks afford you the flexibility to go looking in a extra pinpointed, delicate, and precise manner, whereas retaining the massive context that you simply wanted for reasoning. For instance, you’ll have an extended analysis article, and the sub-chunk on one piece of content material in that article stands out as the clarification of 1 system in a single lengthy paragraph, thus bettering each precision and interpretability.
Instance Code:
# 2. Sub-chunk Indexing
def sub_chunk_indexing(chunk, sub_chunk_size=25):
phrases = chunk.cut up()
sub_chunks = []
current_sub_chunk = []
current_len = 0
for phrase in phrases:
current_len += len(phrase) + 1
current_sub_chunk.append(phrase)
if current_len >= sub_chunk_size:
sub_chunks.append(” “.be a part of(current_sub_chunk))
current_sub_chunk = []
current_len = 0
if current_sub_chunk:
sub_chunks.append(” “.be a part of(current_sub_chunk))
return sub_chunks
# Sub-chunks for first chunk (as instance)
sub_chunks = sub_chunk_indexing(chunks[0], sub_chunk_size=30)
sub_embeddings = [embed(sub_chunk) for sub_chunk in sub_chunks]
print(“Sub-chunks:n”, sub_chunks)
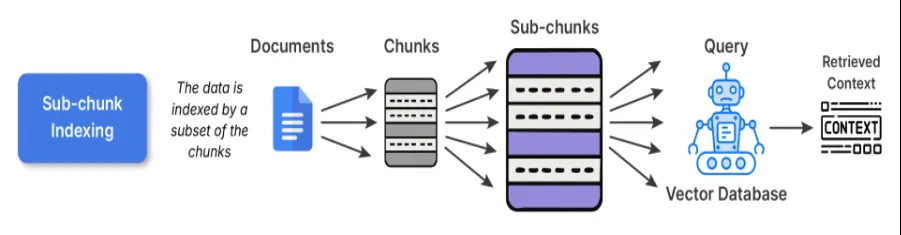
When to make use of: This might be advantageous for datasets that comprise a number of distinct concepts in every paragraph; for instance, if you happen to contemplate information bases-like textbooks, analysis articles, and so forth., this could be ultimate.
Commerce-off: The associated fee is barely larger for preprocessing and storage because of the overlapping embeddings, nevertheless it has considerably higher alignment between question and content material.
3. Question Indexing
Within the case of question indexing, the uncooked textual content will not be straight embedded. As an alternative, we create a number of imagined questions that every chunk may reply, then embeds that textual content. That is partly carried out to bridge the semantic hole of how customers ask and the way your paperwork describe issues.
For instance, in case your chunk says:
“LangChain has utilities for constructing RAG pipelines”
The mannequin would generate queries like:
How do I construct a RAG pipeline in LangChain?
What instruments for retrieval does LangChain have?
Then, when any actual consumer asks an analogous query, the retrieval will hit a kind of listed queries straight.
Instance Code:
# 3. Question Indexing – generate artificial queries associated to the chunk
def generate_queries(chunk):
# Easy artificial queries for demonstration
queries = [
“What is Python used for?”,
“Which libraries does Python support?”,
“What paradigms does Python support?”
]
query_embeddings = [embed(q) for q in queries]
return queries, query_embeddings
queries, query_embeddings = generate_queries(doc_text)
print(“Artificial Queries:n”, queries)
Greatest Practices:
When writing index queries, I might recommend utilizing LLMs to provide 3-5 queries per chunk.
You too can deduplicate or cluster all questions which are like make the precise index smaller.
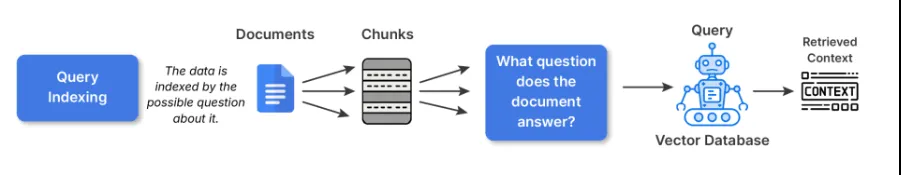
When to make use of:
Q&A methods, or a chatbot the place most consumer interactions are pushed by pure language questions.
Search expertise the place the consumer is more likely to ask for what, how, or why kind inquiries.
Commerce-off: Whereas artificial enlargement provides preprocessing time and house, it supplies a significant increase in retrieval relevance for consumer going through methods.
4. Abstract Indexing
Abstract indexing means that you can reframe items of fabric into smaller summaries previous to embedding. You keep the whole content material in one other location, after which retrieval is finished on the summarized variations.
Why that is useful:
Buildings, dense or repetitive supply supplies (assume spreadsheets, coverage paperwork, technical manuals) generally are supplies that embedding straight from the uncooked textual content model captures noise. Summarizing abstracts away the much less related floor particulars and is extra semantically significant to embeddings.
For Instance:
The unique textual content says: “Temperature readings from 2020 to 2025 ranged from 22 to 42 diploma Celsius, with anomalies attributed to El Nino”
The abstract could be: Annual temperature traits (2020-2025) with El Nino associated anomalies.
The abstract illustration supplies give attention to the idea.
Instance Code:
# 4. Abstract Indexing
def summarize(textual content):
# Easy abstract for demonstration (exchange with an precise summarizer for actual use)
if “Python” in textual content:
return “Python: versatile language, utilized in information science and internet growth with many libraries.”
return textual content
abstract = summarize(doc_text)
summary_embedding = embed(abstract)
print(“Abstract:”, abstract)
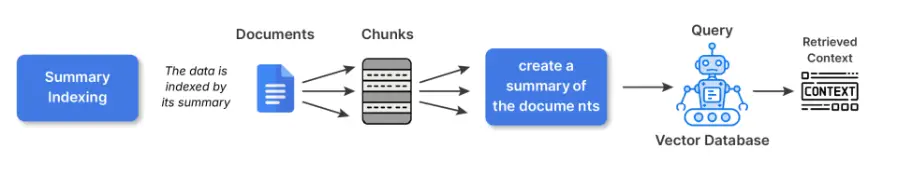
When to make use of it:
With structured information (tables, CSVs, log information)
Technical or verbose content material the place embeddings will underperform utilizing uncooked textual content embeddings.
Commerce off: Summaries can threat shedding nuance/factual accuracy if summaries turn out to be too summary. For essential to area analysis, notably authorized, finance, and so forth. hyperlink to the unique textual content for grounding.
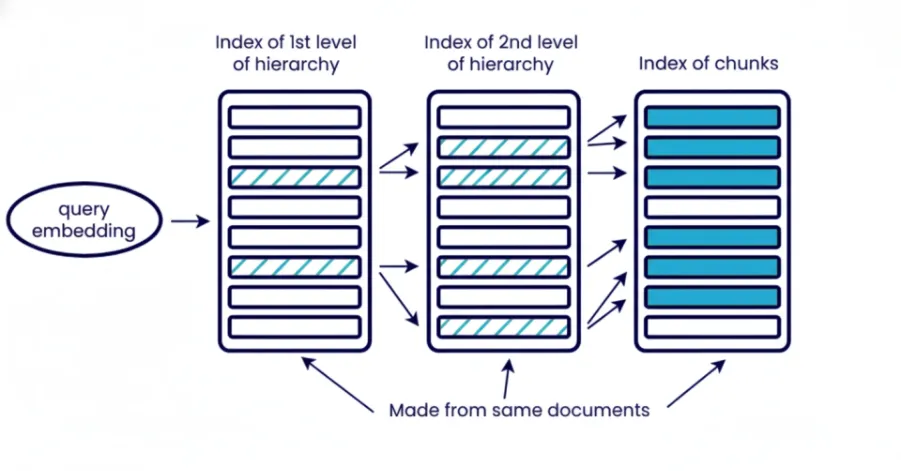
5. Hierarchical Indexing
Hierarchical indexing organizes info into a lot of completely different ranges, paperwork, part, paragraph, sub-paragraph. You retrieve in phases beginning with broad introduce to slim right down to particular context. The highest stage for part retrieves sections of related paperwork and the following layer retrieve paragraph or sub-paragraph on particular context inside these retrieved part of final paperwork.
What does this imply?
Hierarchical retrieval reduces noise to the system and is helpful if you must management the context dimension. That is particularly helpful when working with a big corpus of paperwork and you’ll’t pull it unexpectedly. It additionally enhance interpretability for subsequent evaluation as you’ll be able to know which doc with which part contributed to to the ultimate reply.
Instance Code:
# 5. Hierarchical Indexing
# Manage doc into ranges: doc -> chunks -> sub-chunks
hierarchical_index = {
“doc”: doc_text,
“chunks”: chunks,
“sub_chunks”: {chunk: sub_chunk_indexing(chunk) for chunk in chunks}
}
print(“Hierarchical index instance:”)
print(hierarchical_index)
Greatest Practices:
Use a number of embedding ranges or mixture of embedding and key phrases search. For instance, initially retrieve paperwork solely with BM25 after which extra exactly retrieve these related chunks or parts with embedding.
When to make use of it:
Enterprise scale RAG with 1000’s of paperwork.
Retrieving from lengthy type sources corresponding to books, authorized archives or technical pdf’s.
Commerce off: Elevated complexity attributable to a number of retrievals ranges desired. Additionally requires extra storage and preprocessing for metadata/summaries. Will increase question latency due to multi-step retrieval and never nicely suited to giant unstructured information.
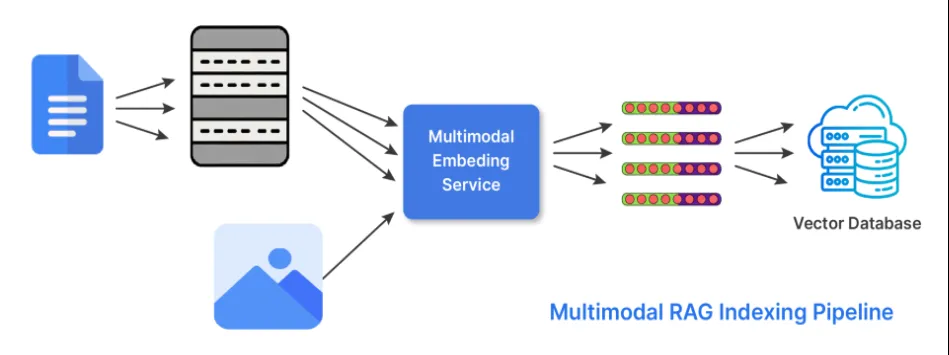
6. Hybrid Indexing (Multi-Modal)
Information isn’t simply in textual content. In its hybrid indexing type, RAG does two issues to have the ability to work with a number of types of information or modality’s. The retriever makes use of embeddings it generates from completely different encoders specialised or tuned for every of the doable modalities. And the fetches outcomes from every of the related embeddings and combines them to generate a response utilizing scoring methods or late-fusion approaches.
Right here’s an instance of its use:
Use CLIP or BLIP for photographs and textual content captions.
Use CodeBERT or StarCoder embeddings to course of code.
Instance Code:
# 6. Hybrid Indexing (instance with textual content + picture)
# Instance textual content and dummy picture embedding (exchange embed_image with precise mannequin)
def embed_image(image_data):
# Dummy instance: picture information represented as size of string (exchange with CLIP/BLIP encoder)
return [len(image_data) / 1000]
text_embedding = embed(doc_text)
image_embedding = embed_image(“image_bytes_or_path_here”)
print(“Textual content embedding dimension:”, len(text_embedding))
print(“Picture embedding dimension:”, len(image_embedding))
When to make use of hybrid indexing:
When working with technical manuals or documentation that has photographs or charts.
Multi-modal documentation or help articles.
Product catalogues or e-commerce.
Commerce-off: It’s a extra sophisticated logic and storage mannequin for retrieval, however a lot richer contextual understanding within the response and better flexibility within the area.
Conclusion
Profitable RAG methods depend upon applicable indexing methods for the kind of information and inquiries to be answered. Indexing guides what the retriever finds and what the language mannequin will floor on, making it a essential basis past retrieval. The kind of indexing you’d use could also be chunk, sub-chunk, question, abstract, hierarchical, or hybrid indexing, and that indexing ought to comply with the construction current in your information, which can add to relevance, and remove noise. Properly-designed indexing processes will decrease hallucinations and supply an correct, reliable system.
Often Requested Questions
A. Indexing encodes information into embeddings, whereas retrieval selects which encoded items the mannequin sees to reply a question.
A. They form how exactly the system can match queries and the way a lot context the mannequin will get for reasoning.
A. Use it when your information base mixes textual content, photographs, code, or different modalities and also you want the retriever to deal with all of them.
Login to proceed studying and luxuriate in expert-curated content material.
Hold Studying for Free







