LLMs like these from Google and OpenAI have proven unimaginable talents. However their energy comes at a price. These large fashions are sluggish, costly to run, and troublesome to deploy on on a regular basis units. That is the place LLM compression methods are available. These strategies shrink fashions, making them quicker and extra accessible and not using a main loss in efficiency. This information explores 4 key methods: mannequin quantization, mannequin pruning strategies, data distillation in LLMs, and Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA), full with hands-on code examples.
Why Do We Want LLM Compression?
Earlier than diving into the “how,” let’s perceive the “why.” Compressing LLMs gives clear benefits that make them sensible for real-world use.
Diminished Mannequin Measurement: Smaller fashions require much less storage, making them simpler to host and distribute.
Sooner Inference: A compact mannequin can generate responses extra rapidly. This improves the consumer expertise in functions like chatbots.
Decrease Prices: Diminished measurement and quicker pace result in decrease wants for reminiscence and processing energy. This cuts down on cloud computing and vitality prices.
Higher Accessibility: Compression permits highly effective fashions to run on units with restricted assets, like smartphones and laptops.
Method 1: Quantization – Doing Extra with Much less
Mannequin quantization is likely one of the hottest and efficient LLM compression methods. It really works by lowering the precision of the numbers (weights) that make up the mannequin. Consider it like saving a high-resolution picture as a compressed JPEG; you lose a tiny quantity of element, however the file measurement shrinks dramatically. Most fashions are educated utilizing 32-bit floating-point numbers (FP32). Quantization converts these to smaller 8-bit integers (INT8) and even 4-bit integers.
This picture visually explains quantization, the place steady, high-precision FP32 (32-bit floating-point) values are mapped to a restricted set of discrete, lower-precision INT4 (4-bit integer) values. Basically, it exhibits how a variety of floating-point numbers are approximated by a smaller, fastened variety of integer ranges to cut back reminiscence and computation, although this could introduce some precision loss.
Fingers-On: 4-bit Quantization with Hugging Face
Let’s quantize a mannequin utilizing the Hugging Face transformers and bitsandbytes library. This instance exhibits methods to load a mannequin in 4-bit precision, considerably lowering its reminiscence footprint.
Step 1: Set up Libraries
First, guarantee you will have the mandatory libraries put in.
!pip set up transformers torch speed up bitsandbytes -q
Step 2: Load and Examine Fashions
We are going to load an ordinary mannequin after which its quantized model to see the distinction.
import torch
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer
# We use a smaller, well-known mannequin for this demonstration
model_id = “gpt2″
print(f”Loading tokenizer for mannequin: {model_id}”)
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_id)
print(“n———————————–“)
print(“Loading unique mannequin in FP32…”)
# Load the unique mannequin in full precision (Float32)
model_fp32 = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(model_id)
# Verify the reminiscence footprint of the unique mannequin
print(“nOriginal mannequin reminiscence footprint:”)
# Calculate reminiscence footprint manually
mem_fp32 = sum(p.numel() * p.element_size() for p in model_fp32.parameters())
print(f”{mem_fp32 / 1024**2:.2f} MB”)
print(“n———————————–“)
print(“Loading mannequin with 4-bit quantization…”)
# Load the identical mannequin with 4-bit quantization enabled
model_4bit = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(
model_id,
load_in_4bit=True,
device_map=”auto” # Robotically makes use of the GPU if accessible
)
# Verify the reminiscence footprint of the 4-bit mannequin
print(“n4-bit quantized mannequin reminiscence footprint:”)
# Calculate reminiscence footprint manually
mem_4bit = sum(p.numel() * p.element_size() for p in model_4bit.parameters())
print(f”{mem_4bit / 1024**2:.2f} MB”)
print(“nNotice the numerous discount in reminiscence utilization!”)
Output:
You’ll discover a big discount within the mannequin’s reminiscence utilization with virtually no change to the standard of its output for many duties.
Method 2: Pruning – Trimming Away Unused Connections
Mannequin pruning strategies work by eradicating components of the neural community that contribute the least to its output. It’s like trimming a plant to encourage more healthy progress. You’ll be able to take away particular person weights (unstructured pruning) or whole teams of neurons (structured pruning). Whereas highly effective, pruning will be complicated to implement accurately.
Unstructured pruning, as an example, removes particular person weights primarily based on their magnitude, making a sparse mannequin. Whereas this makes the mannequin smaller, it may be troublesome for {hardware} to make the most of the sparse construction. Structured pruning removes whole blocks, like neurons or layers, which is commonly extra hardware-friendly.
The picture illustrates completely different methods for pruning parts just like the Imaginative and prescient Transformer (ViT) and the Giant Language Mannequin (LLM) utilizing “pruning layers” to cut back mannequin measurement and enhance effectivity. Particularly, (a) exhibits pruning within the visible encoder, (b) focuses on pruning throughout the LLM, and (c) introduces an “instruction-guided part” to dynamically prune visible tokens primarily based on textual directions, enhancing effectivity for duties like video understanding.
Method 3: Information Distillation – The Pupil-Trainer Method
Information distillation in LLMs is an interesting course of. A big, extremely correct “instructor” mannequin trains a smaller “pupil” mannequin. The scholar learns to imitate the instructor’s thought course of (its output chances), not simply the ultimate reply. This enables the smaller mannequin to attain efficiency far past what it might by coaching on the information alone.
This picture illustrates three data distillation strategies in machine studying: offline, on-line, and self-distillation. Offline distillation makes use of a pre-trained “instructor” to coach a “pupil”, whereas on-line distillation trains each concurrently, and self-distillation includes a single mannequin performing as each instructor and pupil (e.g., deeper layers instructing shallower ones). The orange “instructor” fashions are pre-trained, whereas the blue “pupil” fashions (together with the mixed “instructor/pupil” in self-distillation) are “to be educated”.
Fingers-On: Conceptual Distillation with Hugging Face
Implementing a full distillation pipeline is concerned, however the core concept will be understood by means of the Hugging Face Coach API.
from transformers import TrainingArguments, Coach
# This can be a conceptual instance as an instance the method.
# To run this, you would want:
# 1. An outlined ‘teacher_model’ (a big, pre-trained mannequin).
# 2. An outlined ‘student_model’ (a smaller mannequin to be educated).
# 3. A ‘your_dataset’ object for coaching.
# Outline Coaching Arguments
training_args = TrainingArguments(
output_dir=”./student_model_distilled”,
num_train_epochs=1, # Instance worth
per_device_train_batch_size=8, # Instance worth
# … different coaching arguments
)
# Create a customized Coach to switch the loss operate
class DistillationTrainer(Coach):
def compute_loss(self, mannequin, inputs, return_outputs=False):
# That is the core of information distillation.
# The loss operate is a weighted common of two parts:
# a) The scholar’s commonplace loss on the information (e.g., Cross-Entropy).
# b) The distillation loss, which measures how nicely the scholar’s
# output distribution matches the instructor’s.
# This half is conceptual and requires a full implementation.
print(“Inside customized compute_loss – that is the place distillation logic would go.”)
# For instance:
# student_outputs = mannequin(**inputs)
# student_loss = student_outputs.loss
# with torch.no_grad():
# teacher_outputs = teacher_model(**inputs)
# distillation_loss = some_kl_divergence_loss(student_outputs.logits, teacher_outputs.logits)
# combined_loss = 0.5 * student_loss + 0.5 * distillation_loss
# Returning a dummy loss to stop errors on this conceptual instance
dummy_outputs = mannequin(**inputs)
return (dummy_outputs.loss, dummy_outputs) if return_outputs else dummy_outputs.loss
print(“The DistillationTrainer class is outlined conceptually.”)
print(“A full implementation would require a instructor mannequin, pupil mannequin, and a dataset.”)
This course of successfully transfers the “data” from the big mannequin to the smaller one.
Method 4: Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA) – Environment friendly High-quality-Tuning
Whereas not a way to shrink a base mannequin, Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA) is a way to compress the adjustments made throughout fine-tuning. As an alternative of retraining all of the billions of parameters in a mannequin, LoRA freezes the unique mannequin and injects tiny, trainable “adapter” layers. These adapters are a lot smaller, making the fine-tuning course of quicker and the ensuing fine-tuned mannequin rather more memory-efficient to retailer and swap between.
This diagram explains LoRA (Low-Rank Adaptation) for environment friendly mannequin fine-tuning: throughout coaching, a small, trainable low-rank adaptation matrix (BA) is added to the frozen pretrained weights (W). After coaching, this low-rank matrix is merged with the unique weights, successfully making a specialised mannequin (W + BA) with out growing inference latency or reminiscence footprint throughout deployment. This considerably reduces computational assets and storage necessities in comparison with full fine-tuning.
Fingers-On: High-quality-Tuning with LoRA and PEFT
The Hugging Face PEFT (Parameter-Environment friendly High-quality-Tuning) library makes making use of LoRA easy.
Step 1: Set up Libraries
!pip set up peft -q
Step 2: Apply LoRA and Examine Parameter Counts
from peft import get_peft_model, LoraConfig, TaskType
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM
model_id = “gpt2”
mannequin = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(model_id)
# Outline the LoRA configuration
lora_config = LoraConfig(
task_type=TaskType.CAUSAL_LM, # Specify the duty sort
r=8, # Rank of the replace matrices. Decrease rank means fewer parameters.
lora_alpha=32, # A scaling issue for the realized weights.
lora_dropout=0.1, # Dropout likelihood for LoRA layers.
target_modules=[“c_attn”] # Apply LoRA to the eye layers of GPT-2.
)
# Wrap the bottom mannequin with the LoRA adapters
lora_model = get_peft_model(mannequin, lora_config)
print(“— Authentic Mannequin —“)
# Get the full variety of parameters for the unique mannequin
total_params = sum(p.numel() for p in mannequin.parameters())
print(f”Whole parameters: {total_params:,}”)
print(“n— LoRA Tailored Mannequin —“)
# The PeftModel object has the print_trainable_parameters technique
lora_model.print_trainable_parameters()
print(“nNote how LoRA reduces trainable parameters by over 99%!”)
print(“This makes fine-tuning rather more environment friendly.”)
Output:
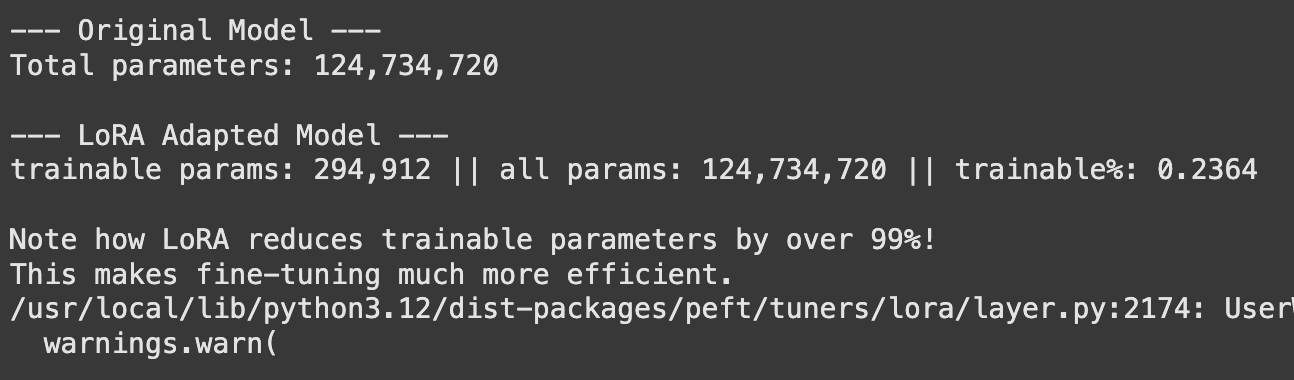
The output will present a dramatic discount (usually over 99%) within the variety of parameters that should be educated and saved. This makes it doable to fine-tune and handle many various variations of a mannequin for numerous duties with out storing large mannequin information for every one.
Yow will discover the total Colab pocket book right here: Colab
Conclusion
Giant Language Fashions are right here to remain, however their large measurement presents an actual problem. LLM compression methods are the important thing to unlocking their potential for a wider vary of functions. Whether or not it’s the easy strategy of mannequin quantization, the surgical precision of mannequin pruning strategies, the intelligent mentorship of information distillation in LLMs, or the effectivity of Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA), these strategies make AI extra sensible. The suitable method depends upon your particular wants, however combining them can usually result in the perfect outcomes.
Continuously Requested Questions
A. Mannequin quantization, particularly Submit-Coaching Quantization (PTQ), is usually the best. Libraries like bitsandbytes mean you can load a quantized mannequin with a single line of code.
A. It might barely scale back accuracy, however for a lot of functions, the loss is minimal and sometimes unnoticeable. Methods like Quantization-Conscious Coaching (QAT) will help protect accuracy even additional.
A. Sure, and it’s usually beneficial. A typical and efficient workflow is to first prune a mannequin, then quantize the consequence, and use data distillation to fine-tune and recuperate any misplaced efficiency.
A. Pruning removes whole connections (weights) from the mannequin, making it sparser. Quantization reduces the numerical precision of all weights with out altering the mannequin’s structure.
A. LoRA doesn’t shrink the unique base mannequin. As an alternative, it compresses the difference or fine-tuning course of, permitting you to create light-weight, task-specific mannequin variations which are a lot smaller than the unique.
Login to proceed studying and revel in expert-curated content material.
Maintain Studying for Free







